Symphonic collaboration
Symphonic collaboration is a paradigm for organizations that build strong cultural norms, values and behavior. As a result they share a strong sense of belonging to a community.
I called this symphonic collaboration, drawn from the example of the symphony orchestra. A world class symphony orchestra, achieves musical harmony that transcends the contribution of any individual or group, for example violinists, in the orchestra. It combines individual brilliance with a synergy of the entire team of musicians. It has several leaders, the most noticeable being the conductor, but there is also the orchestra leader (quite often the first violinist) who conducts the training of the orchestra, and leaders of individual orchestral sections. The orchestra has structure, in terms of both the sections of instruments, e.g. strings, percussion, wind, and its leadership. But this does not enforce rigidity. It aims for conformity and collaboration, but allows creativity and individual inspiration.
The collaboration between the orchestra’s members is technical, willing and passionate.The level of collaboration in a symphony orchestra goes beyond that in most organizations, where departmental or section fiefdoms and empires often clash with each other. While enterprises realize that collaboration is important, it is normally organized on a rational work and technical basis. A symphony orchestra collaborates on both technical and emotional basis. Orchestras have one big advantage: the musicians enjoy their work. When people enjoy their work, they are motivated to do their best and to improve.
Building a culture that motivates people is the way to strive for symphonic collaboration.
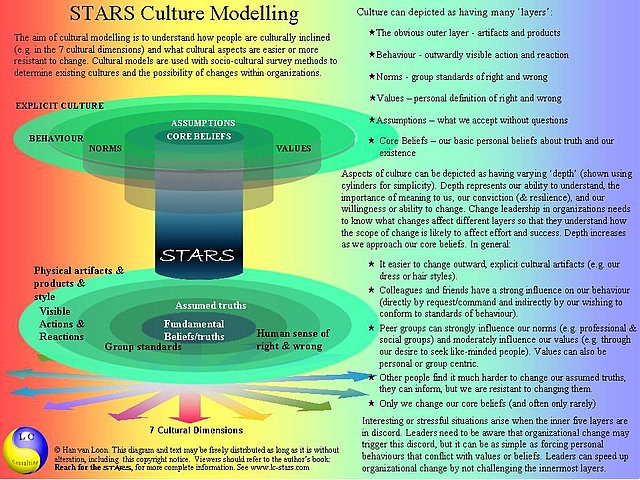
Understanding the existing culture is the first step towards achieving symphonic collaboration. A good socio-cultural survey highlights the various sub-cultures throughout the organization. When an enterprise strives for symphonic collaboration, they compare the existing culture to the desired culture. The survey highlights where cultural change is small and easy or where it is great and difficult. The survey provides information that helps the enterprise plan the actions needed to achieve the desired cultural change.
The techniques such as TIMEWhirlpool can be used to help with forming the goals for a desired organizational culture and the specific aims and means for symphonic collaboration.
The STARS Cultural theme supports and builds upon the STARS Team theme. Symphonic collaboration builds team synergy across the organization. Hence, the benefits of team synergy are replicated and multiply as more of the organization adopts symphonic collaboration.
STARS Cultural theme
The STARS culture theme focuses on socio-cultural management within enterprises. Culture can vary widely between people, professions, organizations, regions and nations. Each impacts to some extent on the other.
For organizations, it is important to understand their own culture in order to optimize the contribution that people make to the organization's vision and mission. The culture affects the way that traditional management disciplines (e.g. quality management, information management, process management) are best implemented. The organizational culture has an even greater effect upon how to implement knowledge and improvement. This is because both are intensely people oriented.
This approach is far superior to the commonly used change management discipline. The problem with change management as practiced by all the large consulting forms, is that the intention is always to implement change, without really understanding the existing enterprise culture. This is why enterprises waste millions on change management iniatives that result in temporary change and poor results. Of course the change consultants love this, because they then have more work!
In STARS, the cultural theme proposes socio-cultural survey, using a variety of means to form a clearer understanding of the existing culture. This highlights norms and values, both across the organization and for various departments, sections, business units and teams (i.e. sub-cultures).
It covers how training helps create shared experiences which in turn help to shape the culture of the organization and the people who comprise it. It looks at how to motivate people to achieve better outcomes and how organization wide synergies lead to symphonic collaboration. For organizations that seek to improve their overall performance, STARS helps focus change leadership on the key success factors required.
The combination of the STARS cultural theme and the Sustainable Improvement theme provide effective improvement.
The combination of the STARS cultural theme and the STARS Knowledge cycle provide 'culturally sensitive knowledge management and foster improvement 'from within'.
STARS cultural modeling combines the work of existing cultural experts with unique elements to help leaders and managers understand the benefits of socio-cultural survey in planning and leading change management in organizations. In particular, it can benefit improvement in organizationally and geographically dispersed networks.
You are welcome to download the linked diagram: STARS Cultural Model on the basis that you respect and display the copyright of the author. You may distribute or link to this diagram, so long as it is not altered in any way.
Corporate culture
STARS in a corporation
- reach-for-the-stars.pdf278 KB